Describes How the Nucleotide Bases Are Paired Together
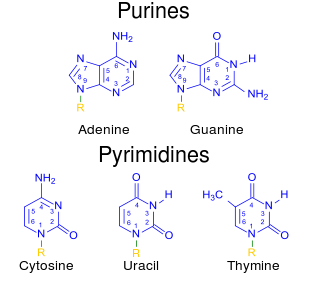
Describes how the nucleotide bases are paired together purines include the nucleotide bases adenine and guanine point mutation when a base is substituted for another during paring which can change the function of the protein or completing stop it from being made e-site location on ribosome in which the tRNA leaves RNA. How are bases paired together in DNA.
What Are The Three Parts Of A Nucleotide Albert Io
Molecule that holds instructions for building a.
. Location on ribosome in which the tRNA leaves. The number 5 carbon of the sugar bonds to the phosphate group. The nucleotides are identical except for the base which can be one of four bases.
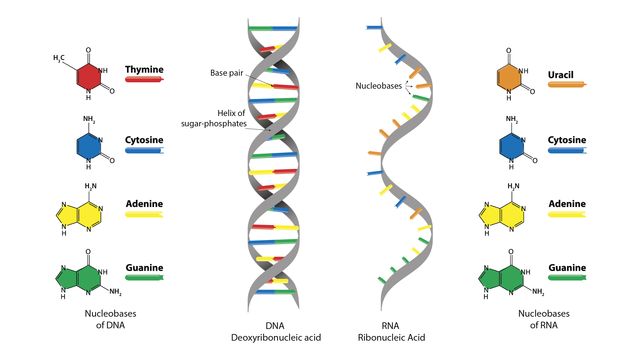
In DNA there are four nitrogenous base options. How do you describe the basic structure of. Bases There are four types of bases in DNA.
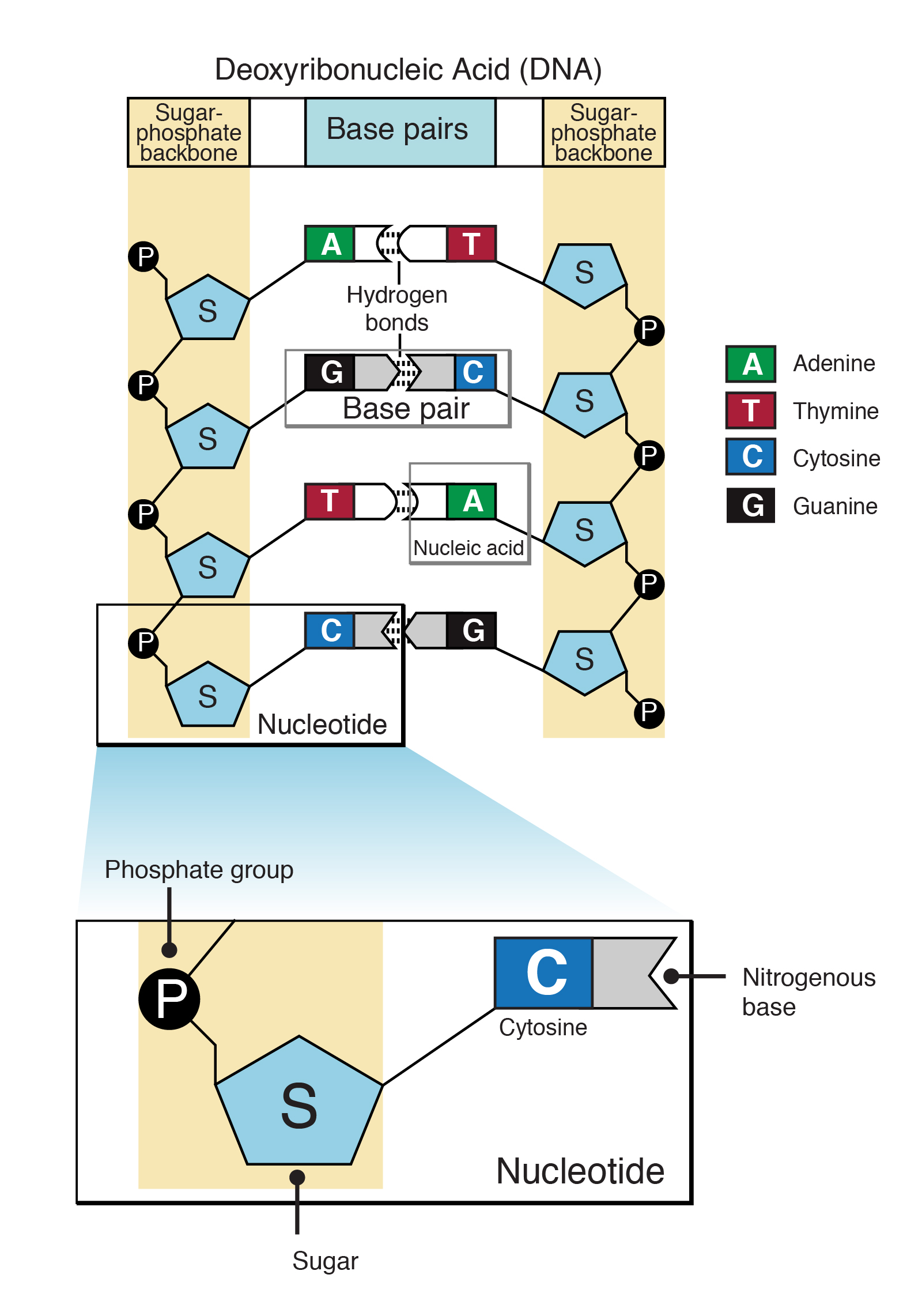
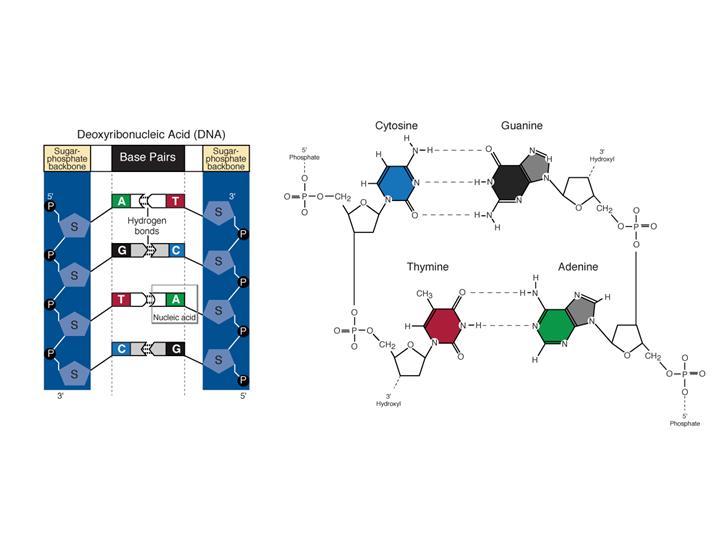
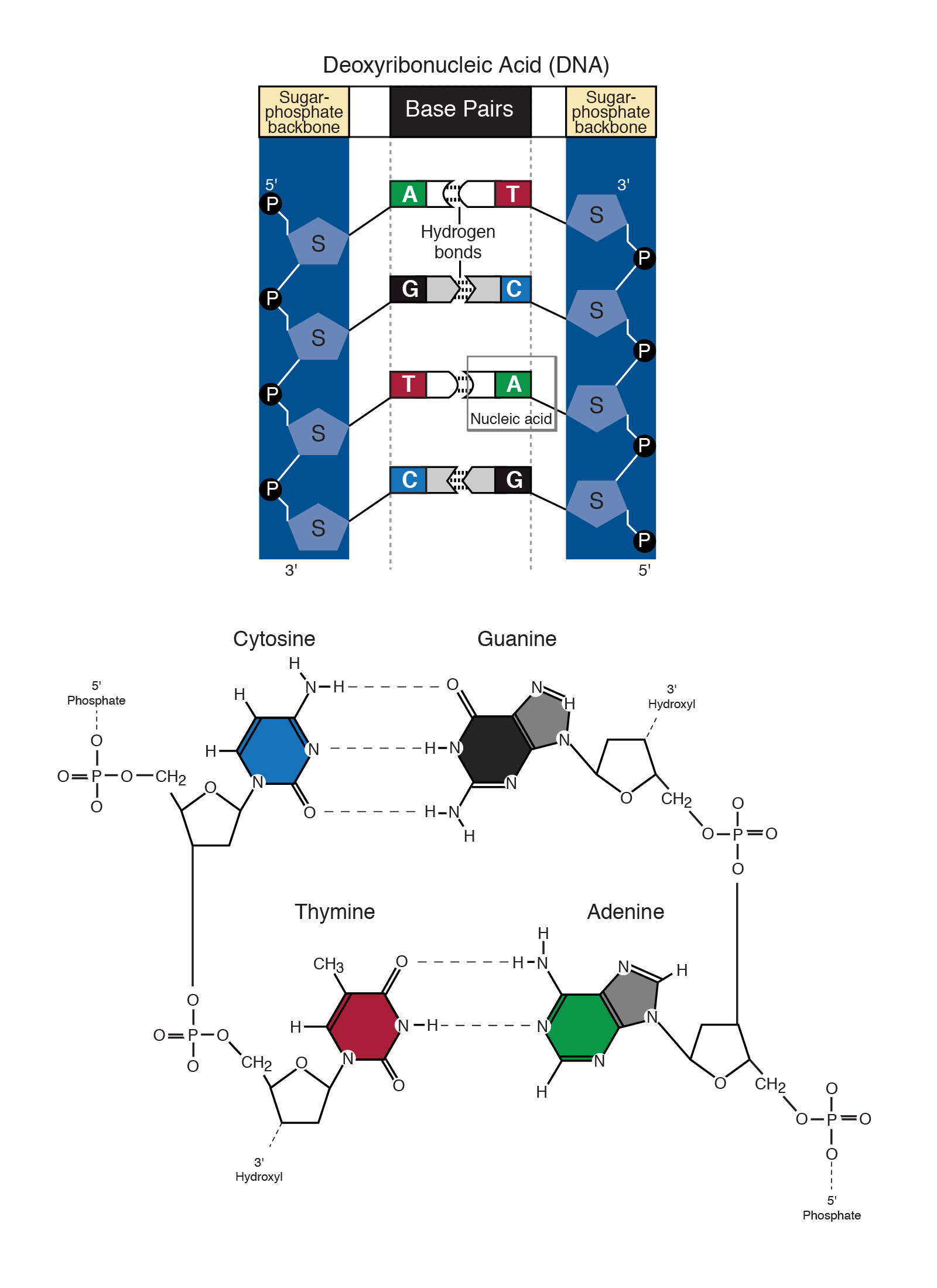
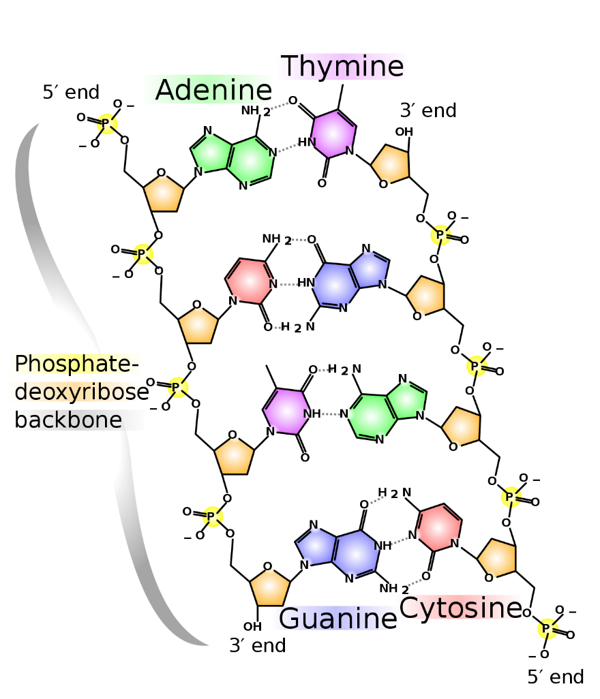
If DNA were thought of as a spiral staircase the base pairs would be the steps. A free nucleotide may have one two or three phosphate groups that attach as a chain to the sugars 5-carbon. The paired bases are held together by hydrogen bonds.
These interactions are specific. So each DNA molecule is made up of two strands and there are four nucleotides present in DNA. Do the 9-2 Now Solve This.
And each of the nucleotides on one side of the strand pairs with a specific nucleotide on the other side of the strand and this makes up the double helix. Chargaff found that there is typically an equivalent number of adenine and thymine bases and an equivalent number of guanine and cytosine bases. Other than this in a nucleotide there is a pentose sugar and a phosphate group too.
Once the incorrect nucleotide has. The nitrogenous bases of the DNA always pair up in specific way purine with pyrimidine A with T G with C held together by weak hydrogen bonds. Due to DNAs double-helical structure the nucleotide bases are paired.
When a base is substituted for another during pairing which can change the function of the protein or completing stop it from being made. This is performed by the exonuclease action of DNA pol III. The hydrogen bonding between complementary bases holds the.
Refer to the related link below for an illustration. Purine-purine links do not form because these bases are too large to fit in the space between the polynucleotide strands. This is called the complementary base pairing rule or Chargaffs rule.
Nucleotides join together in the DNARNA backbone via phosphodiester bonds. Asymmetry in the structure of non-complimentary. Nucleotides form a pair in a molecule of DNA where two adjacent bases form hydrogen bonds.
Complementary base pairings are also responsible for the double-helix. Asymmetry in the structure of non-complimentary. These nitrogenous bases in conjugation with a deoxyribose sugar are called nucleosides.
A free nucleotide may have one two or three phosphate groups attached as a chain to the 5-carbon of the sugar. Base pair describes the relationship between the building blocks on the strands of DNA. Is this a stable interaction that holds the two polynucleotides together.
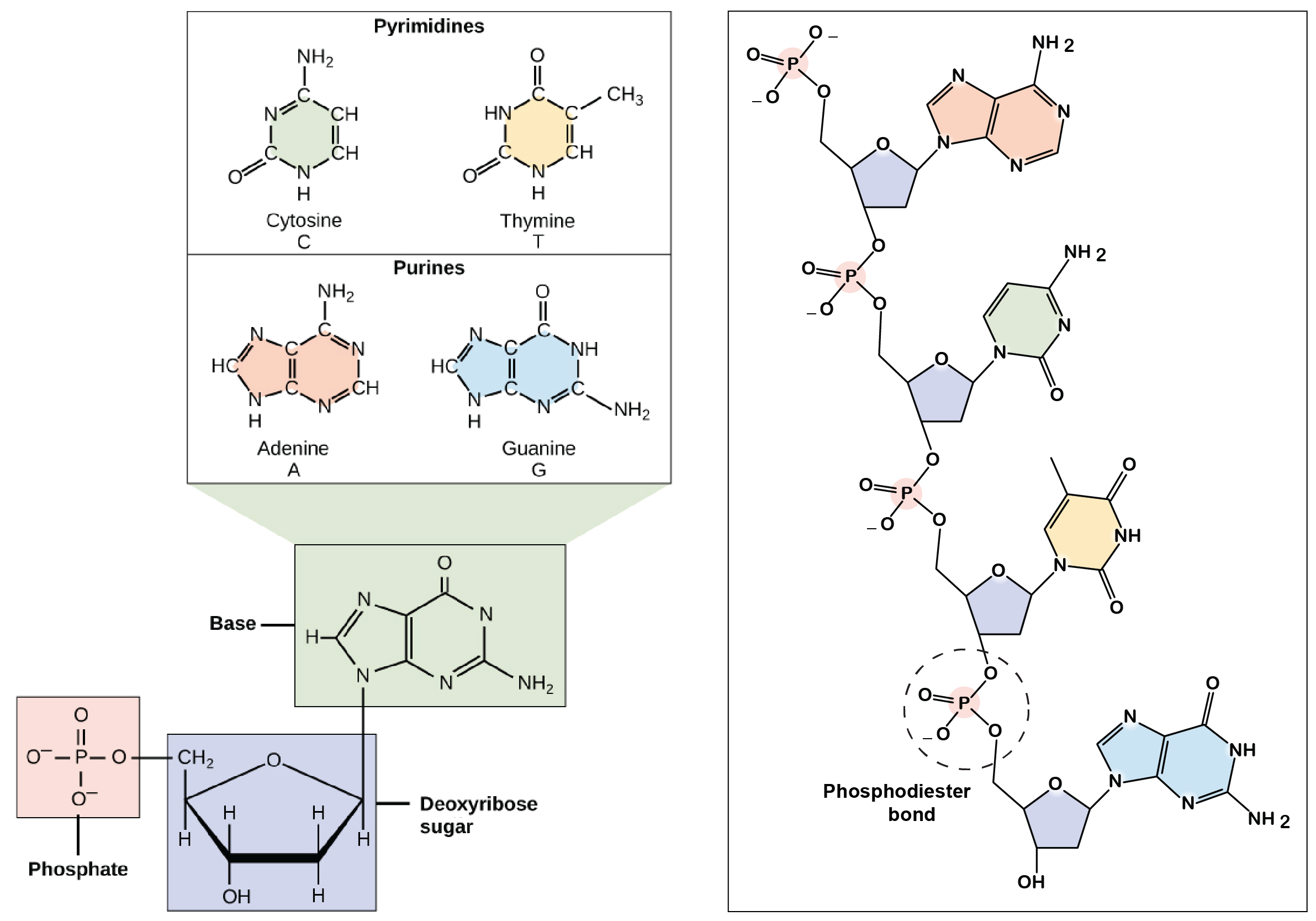
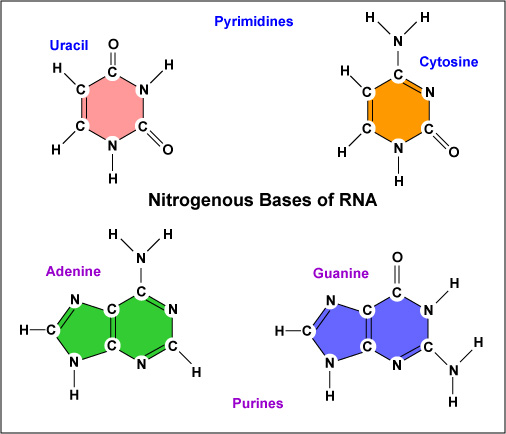
Include the nucleotide bases adenine and guanine. Base is the most important and functional unit. Adenine A thymine T cytosine C and guanine G.
Purine-purine links do not form because these bases are too large to fit in the space between the polynucleotide strands. There are chemical cross-links between the. So for example if theres a G.
Pyrimidine-pyrimidine pairings do not occur because these relatively small molecules do not get close enough to form hydrogen bonds. When they gain one or more phosphate groups they are then termed as nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar deoxyribose in the middle of a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base.
Hydrogen-bond interactions between the bases allow two strands of DNA to form the double helix. A chemical bond between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the sugar of a neighboring nucleotide holds the backbone together. If it is the right base the next nucleotide is added.
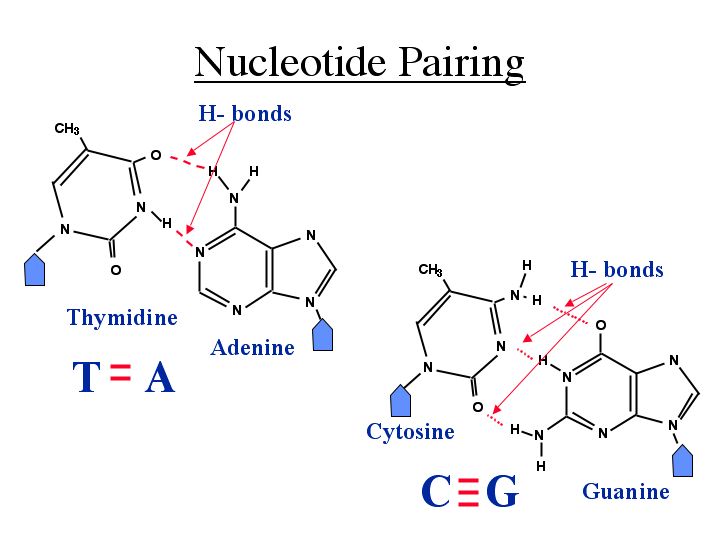
Complementary pairs always involve one purine and one pyrimidine base. Due to the presence of deoxygenated. Adenine is paired with thymine and guanine is paired with cytosine.
Two months after publishing their famous 1953 paper Watson and Crick proposed a model for what. This occurs via hydrogen bonds which are shown with dotted lines in the figure above. Its bonding between the nitrogenous bases that allows for this structure to form.
Base is a heterocyclic ring containing nitrogen. Nitrogenous base is a part of a nucleotide. The A-T pair forms two hydrogen bonds.
Each base can only bond with one other A with T and C with G. In DNA base pairs loosely couple across the double-helix via hydrogen bonds. A base pairs with T and C base pairs with G.
Complementary pairs always involve one purine and one pyrimidine base. Answer 1 of 5. The width of each step is approximately.
How are nucleotide pairs bonded. A C T and G. The nitrogenous bases bonds to the first or primary carbon atom of the sugar.
Nucleotides use these phosphate groups to link together via the formation of phosphodiester bonds and bond to their complementary bases using hydrogen bonds. When nucleotides connect to form DNA or RNA the phosphate of one nucleotide attaches via a phosphodiester bond to the 3-carbon of the sugar of the next nucleotide forming the sugar-phosphate backbone of the nucleic acid. Describes how the nucleotide bases are paired together.
The C-G pair forms three. The nucleotides in a base pair are complementary which means their shape allows them to bond together with hydrogen bonds. The polymerase checks whether the newly added base has paired correctly with the base in the template strand.
Chemical bonds hydrogen bonds between the bases that are across from one another hold the two strands of the double helix together. If an incorrect base has been added the enzyme makes a cut at the phosphodiester bond and releases the wrong nucleotide. In a given sample of DNA all adenine residues will have thymine counterparts on the.
Pyrimidine-pyrimidine pairings do not occur because these relatively small molecules do not get close enough to form hydrogen bonds. The nucleotides in a base pair are complementary which. The Four Nitrogenous Bases.
Base pairing The nucleotides are identical except for the base which can be an adenine thymine guanine or cytosine. Complementary base pairing describes the manner in which the nitrogenous bases of the DNA molecules align with each other.
What Rule Is Used To Join The Free Nucleotides To The Exposed Bases Of The Dna Socratic
What Is A Nucleotide Base Known As A Quora
Are The Nucleotides In Dna There Randomly Or Are They In A Specific Order To Code For Proteins Quora

The Three Phases Of Nucleotide Base Pairing In The Mrna Cds The Download Scientific Diagram
9 1 The Structure Of Dna Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition

Nucleic Acid Deoxyribonucleic Acid Dna Britannica
Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks

Hydrogen Bonding In Dna Base Pairs

Mb Ch 5 Pt 2 Adaptive Follow Up Set 3 Flashcards Quizlet
9 1 The Structure Of Dna Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
Discovery Of The Structure Of Dna Article Khan Academy

Structure And Function Of Dna Microbiology
Fact Sheet Dna Rna Protein Microbenet The Microbiology Of The Built Environment Network
Comments
Post a Comment